Permanent
in colour- Fibre Reactive Dyes
can
be easily said to be the most permanent of all dye types. This is
because of an unique quality, unlike other dyes, it can actually form a
covalent bond with the Substrate (cellulose or protein molecule). After
the formation of the bond, there is only one molecule, as the molecule
of the is now part of the cellulose fiber molecule.
 Easy
washing-
Easy
washing- The fibres that are
dyed with reactive dyes can be
safely dyed even with white garments without the danger of colouring
it.
 Chemical
Binding-
Chemical
Binding- The chemical bonds as
explained above significantly
improves the product's colour stability and washability. Thus, no doubt
reactive dying of cotton is presently the most popular textile dying
process in the world.
- Classification
of Reactive Dyes
Reactive dyes can be
classified as
following_
Vinylsulphone Dye (VS)- Vinylsulphone
Dyes are moderately
reactive. The dyeing temperature is generally 600C and pH is 11.5 that
gets applied by utilising a mixture of soda ash and caustic soda. These
dyes show excellent fixation properties under proper alkaline
condition. A typical example is the Remazol Black B (CI Reactive Black
5)
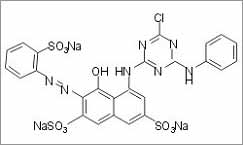
 Monochlorotriazine
Dye (MCT)-
Monochlorotriazine
Dye (MCT)- Normally these dyes
are less reactive than
vinylsulphone dyes. Reaction can take place in more energetic reaction
conditions. That is typically 800C and pH value of 10.5, are essential
for a proper fixation on cellulosic fibres. A typical
monochlorotriazine dye is shown here.
Bi-functional Dye-
A Bi-functional dye is a form of reactive
dye that shows more than one type of reactive group in the molecule.
These reactive dyes are designed in such a manner to have the capacity
to react with the fibre in more than a single way
Reactive
dyes are used to dye
cellulosic fibres. The dyes contain a reactive group, either a haloheterocycle
or an activated double bond,
that, when applied to a fibre in an alkaline
dye bath, forms a chemical bond with an hydroxyl group on the
cellulosic fibre.
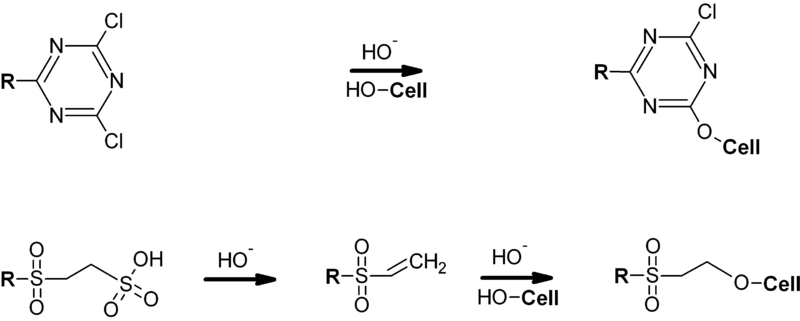
R
= Chromophore
Cell
= Cellulose
Reactive
dyeing is now the most
important method for the coloration of cellulosic fibres. Reactive dyes
can also be applied on wool and nylon; in the latter case they are
applied under weakly acidic
conditions. Reactive dyes have a low utilization degree compared to
other types of dyestuff, since the functional group also bonds to
water, creating hydrolysis.
Reactive
dyes are categorized by
functional group[1].
| Functional Group |
Fixation |
Temperature |
Included in Brands |
| Monochlorotriazine |
Haloheterocycle |
80˚ |
Basilen E & P
Cibacron
E
Procion H,HE |
| Monofluorochlorotriazine |
Haloheterocycle |
40˚ |
Cibacron F & C |
| Dichlorotriazine |
Haloheterocycle |
30˚ |
Basilen M
Procion MX |
| Difluorochloropyrimidine |
Haloheterocycle |
40˚ |
Levafix EA
Drimarene
K & R |
| Dichloroquinoxaline |
Haloheterocycle |
40˚ |
Levafix E |
| Trichloropyrimidine |
Haloheterocycle |
80-98˚ |
Drimarene X & Z
Cibacron T |
| Vinyl sulfone |
activated double bond |
40˚ |
Remazol |
| Vinyl amide |
activated double bond |
40˚ |
Remazol |